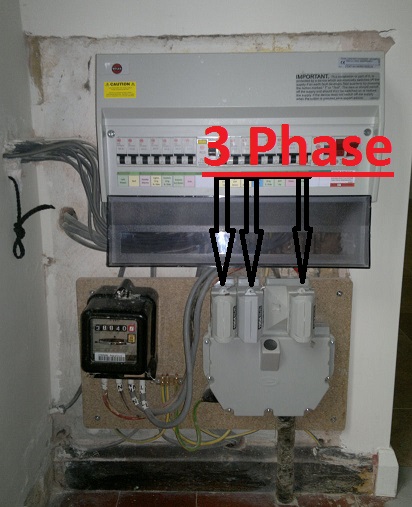
A generator manual transfer switch in the UK connects your standby generator to the mains supply safely and securely. Blades Power Generation supplies these switches with precision engineering.
Why Choose a Manual Transfer Switch Over Basic Options
Manual switches demand user intervention. You flip the switch when the grid fails. This control prevents backfeeding. Our models feature interlocks that block simultaneous connections.
Installation fits most UK properties. Electricians wire them into consumer units. Panels handle currents ranging from 63 amps to 200 amps. Sub-main feeds integrate seamlessly. Generators up to 50 kVA pair perfectly.
Durability stands out. Enclosures rate IP65 for outdoor use. Blades sources components from European manufacturers.
Transition to Automatic Systems for Seamless Operation
Manual control works for occasional use. Frequent outages need more. Buy an Automatic Transfer Switch in the UK from Blades for zero downtime. These units detect mains failure in milliseconds. They start the generator and transfer the load automatically.
Controllers use microprocessor technology. Voltage sensing covers 180-270V ranges. Frequency monitoring ensures stability at 50Hz. Transfer time stays under 10 seconds. Return to mains happens without manual input.
Key Features in Our Automatic Transfer Switches
Advanced models include programmable delays. Start delay avoids nuisance trips. Cool-down periods protect engines. Load shedding prioritises critical circuits.
Integration with BMS systems is standard. Modbus protocols allow remote monitoring. Enclosures match manual counterparts in robustness. Fire-rated options meet building codes.
Generator compatibility spans diesel, gas, and hybrid units. Synchronisation modules handle parallel operation. This suits larger installations such as data centres.
Compliance and Safety Standards Specific to UK Installations
Every switch carries a UKCA marking. Third-party testing verifies performance. Overload protection trips at 110% rating. Short-circuit withstand reaches 10kA.
Earthing systems follow TN-S and TN-C-S configurations. Neutral switching prevents floating neutrals. Phase rotation checks stop reverse feeding.
Cost Benefits Over the Switch Lifecycle
Initial outlay recovers quickly. Preventing downtime saves thousands. Insurance premiums drop with proper installation. Energy efficiency rises as generators run optimally.
Generator manual transfer switches in the UK switches start at competitive prices. Automatic versions scale with features. Volume orders reduce unit costs for contractors.
Future-Proofing Your Power Infrastructure
Smart grid developments evolve rapidly. Our switches support AMI protocols. Load management prepares for demand response schemes.
Electric vehicle charging integrates via dedicated circuits. Transfer switches isolate EVSE during outages. This maintains mobility.
We manufacture in the UK. Lead times stay under four weeks. Custom enclosures match exact requirements. Technical drawings accompany every order.
Training courses certify installers. Online portals access wiring diagrams. Software tools simulate transfer scenarios.
Buy an Automatic Transfer Switch in the UK directly through our portal. Configure specifications online. Receive CAD files instantly. Streamline your backup power project today.